Polymer Products Prices in Iran’s free Market
Polymer products in Iran have become a significant point of interest for manufacturers, traders, and buyers both inside the country and across international markets. As one of the Middle East’s key players in petrochemical production, Iran hosts a variety of polymer-producing companies supplying high-quality raw materials at competitive prices.
In this article, we explore the current state of polymer pricing in Iran, the factors that affect price trends, key polymer types available in the market, and insights for buyers who rely on timely and accurate pricing to manage supply chains and costs.
Note: The prices in this article are calculated based on an exchange rate of 1,077,000 Iranian rials per US dollar. Please keep in mind that any fluctuations in the exchange rate will affect the USD-equivalent prices.
Date: Wednesday, 05 November 2025
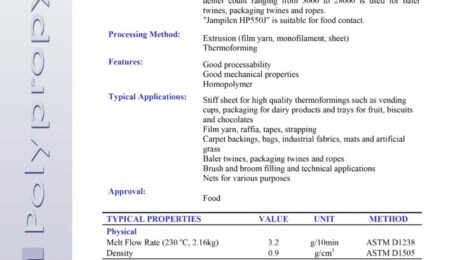
| Polymer Grade | Company | Price (USD/tonne) | Datasheet Analysis |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0035 | Bandar Imam | $833 | 0035 Datasheet |
| 6200 | Miandoab | – | 6200 Datasheet |
| BL3 | Marun | $836 | BL3 Datasheet |
| BL3 | Bakhtar | $833 | BL3 Datasheet |
| BL3 | Jam | $808 | BL3 Datasheet |
| 3840 | Tabriz | $785 | 3840 Datasheet |
| F7000 | Mehr | $871 | F7000 Datasheet |
| F7000 | Ilam | $865 | F7000 Datasheet |
| F7000 | Miandoab | $824 | 7000F Datasheet |
| F7000 | Bandar Imam | – | F7000 Datasheet |
| 5110 | Arya Sasol | $819 | 5110 Datasheet |
| 5510 | Arya Sasol | $789 | 5510 Datasheet |
| X5 | Marun | $817 | EX5 Datasheet |
| X5 | Jam | – | EX5 Darasheet |
| X5 | Bakhtar | $791 | EX5 Datasheet |
| X3 | Amir Kabir | $864 | EX3 Datasheet |
| P100(n) | Jam | $877 | PE100 Datasheet |
| P100(b) | Shazand | $887 | PE100 Datasheet |
| 020 | Bandar Imam | $970 | LF0200 Datasheet |
| 075 | Bandar Imam | $1,021 | 075 Datasheet |
| 0190 | Arya Sasol | $941 | 0190 Datasheet |
| 2420(E02) | Kordestan | $916 | 2420E02 Datasheet |
| 2420(H) | Amir Kabir | $903 | 2420 h Datasheet |
| 2102(TX) | Laleh | $933 | L2102TX Datasheet |
| 2100 | Laleh | – | 2100 Laleh |
| LLD 209 | Amir Kabir | $970 | LL0209AA Datasheet |
| LLD 209 | Shazand | $938 | LL0209AA Datasheet |
| LLD22B02 | Mahabad | $915 | 22B02 Datasheet |
| LLD22B02 | Lorestan | – | 22B02 Datasheet |
| 235(F6) | Jam | $910 | 22B02 Datasheet |
| 52518 | Jam | $782 | HD52518 Datasheet |
| HI500 | Bandar Imam | $799 | HI0500 Datasheet |
| 54B04 | Lorestan | $761 | 54B04 Datasheet |
| 62n07 | Lorestan | $783 | 62N07 Datasheet |
| 62n07 | Miandoab | $783 | 62N07 Datasheet |
| 1922 | Laleh | $1,393 | 1922T Datasheet |
| C30S | Marun | $1,439 | C30SDatasheet |
| 1102XL | Regal | $1,448 | 1102XL Datasheet |
| 1102XK | Regal | $1,448 | 1102 XK Datasheet |
| 510L | Jam | $1,448 | 510L Datasheet- |
| 510L | Khomeyn | – | 510L Datasheet |
| HP500 | Khomeyn | – | HP500P Datasheet |
| HP500 | Marun | – | HP500P Datasheet |
| 550J | Jam | $1,486 | 550J Datasheet |
| 550J | Khomeyn | – | 550J Datasheet |
| Z30S | Marun | $1,272 | Z30S Datasheet |
| 552R | Jam | $1,272 | HP552R Datasheet |
| 552R | Shazand (Arak) | $1,272 | HP552R Datasheet |
| 552R | Marun | $1,272 | HP552R Datasheet |
| 548T | Jam | $1,263 | 548T Datasheet |
| 548R | Jam | $1,210 | PPC-EP548R-JAM |
| 548R | Navid Zar Shimi | – | EP548R Datasheet |
| 440L | Jam | $1,214 | 440L Datasheet |
| 440G | Jam | $1,513 | 440G Datasheet |
| 3130 | Jam | – | 3130uv Datasheet |
| R40 | Shazand (Arak) | $1,179 | R40 Datasheet |
| RP340 | Jam | $1,096 | RP340 Datasheet |
| RP340 | Marun | $1,096 | RP340N Datasheet |
| RP345 | Jam | $1,096 | 345S Datasheet |
| ZR340 | Navid Zar Shimi | $1,096 | ZR340R Datasheet |
| ZR230 | Navid Zar Shimi | $1,448 | ZR230 Datasheet |
| MR230 | Marun | $1,448 | Mr230 Datasheet |
| MR270 G | Shazand | – | |
| RP210 G on-grade | Shazand | $1,532 | RP210G Datasheet |
| RP210 G off-grade | Shazand | $1,235 | RP210G Datasheet |
| RP210 G | Marun | – | RP210G Datasheet |
| ABS 150 | Tabriz | $1,277 | ABS150 Datasheet |
| ABS N50 | Ghaedbasi | $1,305 | ABS50N Datasheet |
| 7240 | Tabriz | $887 | HIPS 7240 Datasheet |
| 6045 | Petro Paak | $887 | GPPS 1115 Petropaak |
| 1540 | Tabriz | $799 | GPPS 1540 Datasheet |
| 1551 | Takhte Jamshid | $775 | GPPS1551 Datasheet |
| 1115 | Petro Paak | $780 | GPPS1115 Datasheet |
| 3160 | Jam | $731 | GPPS 3160 Daasheet |
| PVC | Bandar Imam | $687 | PVC S65 Datasheet |
| PVC | Arvand | $687 | PVC S65 Datasheet |
For visiting the prices of Polymer materials in Iran’s free market, please click on the following link: Prices of Polymer Products in Iran’s free market
Iran’s Role in the Global Polymer Market
Iran is a leading producer of polymer raw materials, thanks to its access to vast natural gas and oil resources, which serve as the feedstock for polymer manufacturing. Major companies such as Jam Petrochemical, Marun, Bandar Emam, Arya Sasol, Shazand, Ilam, and Tabriz Petrochemical are regularly listed among the top suppliers of polyethylene (PE), polypropylene (PP), polystyrene (PS), PVC, and ABS.
Iran’s geographic location offers export access to nearby markets including Turkey, Central Asia, India, China, and Europe. However, even with growing demand for Iranian polymer products, local price fluctuations are affected by a range of domestic and global variables.
Main Types of Polymers and Their Pricing
The Iranian polymer market covers a wide spectrum of products, including:
- HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene)
- LDPE (Low-Density Polyethylene)
- LLDPE (Linear Low-Density Polyethylene)
- PP (Polypropylene)
- PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride)
- ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene)
Each of these materials has subgrades depending on their use in injection molding, blow molding, film production, pipe extrusion, and more.
Let’s break down each category in terms of price trends and market availability.
HDPE Prices in Iran
HDPE grades such as 0035, 5110, 5502, and 52518 are among the most traded in Iran. These are used in packaging, containers, tanks, and household products. Prices are influenced by international oil prices, currency exchange rates (especially the USD to IRR rate), and local supply/demand balance.
HDPE prices in Iran typically range from $780 to $900 per ton, depending on the grade and producer. For example, HDPE 0035 from Bandar Emam is usually priced competitively, making it popular among bulk buyers.
LDPE & LLDPE Prices
LDPE and LLDPE are primarily used in film applications such as agricultural film, packaging film, and plastic bags. Grades like 2420D, 2420H, LLDPE 22B02, and 209AA are well-known in the Iranian market.
Prices for LDPE/LLDPE range between $850 and $950 per ton, depending on the product specifications and region of supply (e.g., Mahabad, Lorestan, Shazand, or Amir Kabir Petrochemical).
Polypropylene (PP) Prices
Polypropylene is widely used in the automotive industry, food packaging, textiles, and medical applications. Key grades include Z30S, V30S, HP500, RP340, and P100.
The PP price in Iran is relatively volatile due to high export demand and domestic consumption. Currently, prices vary between $1,000 and $1,300 per ton. For high-performance PP copolymers and random copolymers, the price can exceed $1,400.
PVC Prices
PVC 65 is the most commonly traded PVC grade in Iran, often produced by Arvand Petrochemical or Bandar Emam. It’s used in pipe manufacturing, fittings, profiles, cables, and flooring.
PVC prices are somewhat stable, usually ranging from $750 to $850 per ton. However, availability may vary based on seasonality and local infrastructure demand.
ABS Prices in Iran
ABS is in high demand for automotive parts, electronic housings, and consumer goods. Ghaed Basir and Tabriz Petrochemical are the main suppliers.
Due to its reliance on imported feedstock, ABS prices in Iran are relatively high compared to other polymers—typically between $1,700 and $2,000 per ton.

Factors Affecting Polymer Prices in Iran
The pricing of polymer products in Iran depends on several key factors:
- Exchange Rate Volatility
Since many contracts are benchmarked against the U.S. dollar, fluctuations in the USD/IRR exchange rate directly impact prices in local and export markets. - Raw Material Costs
Feedstock availability, particularly ethylene, propylene, and styrene, plays a vital role. Crude oil and naphtha prices are also influential. - Export Regulations and Sanctions
Political and economic sanctions affect international trade flows, influencing both availability and pricing for domestic buyers. - Local Supply and Demand
Industrial demand, seasonal variation, and production shutdowns or maintenance periods at petrochemical plants can cause temporary price shifts. - Government Pricing Policies
Iran’s commodity exchange (IME) sets base prices weekly, providing transparency and a pricing benchmark for domestic trade.
How to Stay Updated on Polymer Prices
Given the daily changes in currency and international feedstock rates, staying updated on polymer prices in Iran requires:
- Daily/weekly market reports
- Direct price updates from petrochemical suppliers
- Monitoring of Iran Mercantile Exchange (IME) announcements
- Telegram groups and online trading forums for fast-moving quotes
If you’re buying in bulk, working with reliable suppliers who can offer updated prices and stock availability is crucial. Here are several reputable international websites that provide global prices for polymer and petrochemical commodities, including real-time market data, analysis, and price trends:
1. ICIS (Independent Commodity Intelligence Services)
- Website: www.icis.com
- Coverage: Polymers (HDPE, LDPE, LLDPE, PP, PVC, PET), petrochemicals (ethylene, propylene, etc.)
- Features: Price benchmarks, market news, analysis, forecasting.
- Note: Requires a subscription for detailed pricing data.
2. Platts (by S&P Global)
- Website: www.spglobal.com/platts
- Coverage: Petrochemical prices, including olefins, aromatics, polymers.
- Features: Daily and weekly assessments, market commentary.
- Note: Professional-level service, subscription required.
3. ChemOrbis
- Website: www.chemorbis.com
- Coverage: Plastic raw materials (HDPE, LDPE, LLDPE, PP, PVC, PS, ABS), global market news.
- Regions: Focus on Middle East, Asia, Europe, Turkey.
- Features: Price indexes, polymer news, import/export data.
- Free access: Limited data; full access requires subscription.
4. Polymerupdate
- Website: www.polymerupdate.com
- Coverage: Daily polymer and petrochemical price assessments for India, Asia, Middle East, Europe.
- Products: HDPE, LDPE, LLDPE, PP, PVC, PET, etc.
- Features: Prices, news, import/export data, reports.
- Note: Paid subscription for full access.
5. PlasticsExchange
- Website: www.theplasticsexchange.com
- Coverage: US-based real-time marketplace for buying/selling polymers.
- Products: HDPE, LDPE, LLDPE, PP, PS, PET.
- Features: Spot pricing, live trading, historical charts.
- Free registration available.
6. Tecnon OrbiChem
- Website: www.orbichem.com
- Coverage: Chemicals and polymers.
- Focus: Strategic market analysis, price forecasts.
- Note: High-level consultancy and data service; subscription required.
7. PIE (Plastics Information Europe)
- Website: www.pieweb.com
- Coverage: Polymers across European markets.
- Features: Daily price updates, analysis, news.
- Note: German-based, strong EU focus, subscription required.
Final Thoughts
The polymer products prices in Iran offer a compelling mix of affordability and quality, making Iranian polymers an attractive option for local and foreign manufacturers. While market dynamics are complex and often change rapidly, understanding the pricing landscape and building a strong network can help buyers make informed, timely decisions.
Whether you’re sourcing HDPE, LDPE, PP, or engineering plastics like ABS, Iran remains one of the best destinations for cost-effective and diverse polymer raw materials. Keeping an eye on USD to IRR rates, local market trends, and government policies will ensure you’re ahead in the game.
- Published in Uncategorized
Polymer Datasheets: Exploring Iran’s Petrochemical Products
Introduction
In the world of plastics, polymer datasheets are essential tools for understanding the properties and applications of materials. Whether you are a polymer buyer, plastic product manufacturer, or a technical procurement manager, you rely on datasheets to make informed decisions. This article dives deep into the polymer products of Iran’s leading petrochemical companies, explaining common materials such as Polyethylene (HDPE, LDPE, LLDPE), Polypropylene (PP), ABS, PVC, GPPS, and HIPS — all with a focus on their technical datasheet values and sourcing information.
| Polymer Grade | Company | Polymer Type/ Process Method | Datasheet Analysis |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0035 | Bandar Emam | HDPE/Blow molding | 0035 Datasheet |
| 6200 | Miandoab | HDPE/Blow molding | 6200 Datasheet |
| BL3 | Marun | HDPE/Blow molding | BL3 Datasheet |
| BL3 | Bakhtar | HDPE/Blow molding | BL3 Datasheet |
| BL3 | Jam | HDPE/Blow molding | BL3 Datasheet |
| BL4 | Bakhtar | HDPE/Blow molding | BL4 Datasheet |
| 3840 | Tabriz | MDPE/ Rotational molding | 3840 Datasheet |
| F7000 | Mehr | HDPE/Film extrusion | F7000 Datasheet |
| F7000 | Ilam | HDPE/Film extrusion | F7000 Datasheet |
| F7000 | Miandoab | HDPE/Film extrusion | 7000F Datasheet |
| 5110 | Arya Sasol | HDPE/Film extrusion | 5110 Datasheet |
| 5510 | Arya Sasol | HDPE/Blow molding | 5510 Datasheet |
| X5 | Marun | HDPE/Film extrusion | EX5 Datasheet |
| X5 | Jam | HDPE/Film extrusion | EX5 Darasheet |
| X5 | Bakhtar | HDPE/Film extrusion | EX5 Datasheet |
| X3 | Amir Kabir | HDPE/Pipe extrusion | EX3 Datasheet |
| P100(n) | Jam | HDPE/Pipe extrusion | PE100 Datasheet |
| P100(b) | Jam | HDPE/Pipe extrusion | PE100 Datasheet |
| P100(b) | Shazand | HDPE/Pipe extrusion | PE100 Datasheet |
| 020 | Bandar Emam | LDPE/Film extrusion | LF0200 Datasheet |
| 075 | Bandar Emam | LDPE/Film extrusion | 075 Datasheet |
| 0190 | Arya Sasol | LDPE/Film extrusion | 0190 Datasheet |
| (E02)2420 | Kordestan | LDPE/Film extrusion | 2420E02 Datasheet |
| (H)2420 | Amir Kabir | LDPE/Film extrusion | 2420 h Datasheet |
| (TX)2102 | Laleh | LDPE/Film extrusion | L2102TX Datasheet |
| 2100 | Laleh | LDPE/Film extrusion | 2100 Laleh |
| LLD 209 | Amir Kabir | LLDPE/Film extrusion | LL0209AA Datasheet |
| LLD 209 | Shazand | LLDPE/Film extrusion | LL0209AA Datasheet |
| LLD22B02 | Mahabad | LLDPE/Film extrusion | 22B02 Datasheet |
| LLD22B02 | Lorestan | LLDPE/Film extrusion | 22B02 Datasheet |
| (F6)235 | Jam | LLDPE/Film extrusion | 22B02 Datasheet |
| 52518 | Jam | HDPE/Injection molding | HD52518 Datasheet |
| 52B18 | Jam | HDPE/Injection molding | 52b18 Datasheet |
| HI500 | Bandar Imam | HDPE/Injection molding | HI0500 Datasheet |
| 54B04 | Lorestan | HDPE/Injection molding | 54B04 Datasheet |
| 62n07 | Lorestan | HDPE/Injection molding | 62N07 Datasheet |
| 62n07 | Mahabad | HDPE/Injection molding | 62N07 Datasheet |
| 62n07 | Miandoab | HDPE/Injection molding | 62N07 Datasheet |
| 1922 | Laleh | LDPE/Injection molding | 1922T Datasheet |
| C30S | Marun | Polypropylene | C30SDatasheet |
| 1102XL | Regal | Polypropylene | 1102XL Datasheet |
| 1102XK | Regal | Polypropylene | 1102 XK Datasheet |
| 510L | Jam | Polypropylene | 510L Datasheet- |
| 510L | Khomeyn | Polypropylene | 510L Datasheet |
| HP500 | Khomeyn | Polypropylene | HP500P Datasheet |
| HP500 | Marun | Polypropylene | HP500P Datasheet |
| 550J | Jam | Polypropylene | 550J Datasheet |
| 550J | Khomeyn | Polypropylene | 550J Datasheet |
| Z30S | Marun | Polypropylene | Z30S Datasheet |
| V30S | Marun | Polypropylene | V30S Datasheet |
| 552R | Jam | Polypropylene | HP552R Datasheet |
| 552R | Shazand (Arak) | Polypropylene | HP552R Datasheet |
| 552R | Marun | Polypropylene | HP552R Datasheet |
| 548T | Jam | Polypropylene | 548T Datasheet |
| 548R | Jam | Polypropylene | PPC-EP548R-JAM |
| 548R | Navid Zar Shimi | Polypropylene | EP548R Datasheet |
| 440L | Jam | Polypropylene | 440L Datasheet |
| 440G | Jam | Polypropylene | 440G Datasheet |
| 3130 | Jam | Polypropylene | 3130uv Datasheet |
| R40 | Shazand (Arak) | Polypropylene | R40 Datasheet |
| RP340 | Jam | Polypropylene | RP340 Datasheet |
| RP340 | Marun | Polypropylene | RP340N Datasheet |
| RP345 | Jam | Polypropylene | 345S Datasheet |
| ZR340 | Navid Zar Shimi | Polypropylene | ZR340R Datasheet |
| ZR230 | Navid Zar Shimi | Polypropylene | ZR230 Datasheet |
| MR230 | Marun | Polypropylene | Mr230 Datasheet |
| RP210(G) | Shazand | Polypropylene | RP210G Datasheet |
| ABS 150 | Tabriz | Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene | ABS150 Datasheet |
| ABS N45 | Ghaedbasir | Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene | ABSN45Datasheet |
| ABS N50 | Ghaedbasi | Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene | ABS50N Datasheet |
| ABS N70 | Ghaedbasir | Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene | ABS N70 Datasheet |
| ABS 10417 | Ghaedbasir | Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene | ABS 10417 Datasheet |
| ABS 10415 | Ghaedbasir | Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene | ABS-10415 Datasheet |
| ABS 10415 | Tabriz | Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene | ABS-10415 Datasheet |
| ABS 10720 (White) | Ghaedbasir | Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene | ABS 10720 Datasheet |
| ABS 90913(Black) | Ghaedbasir | Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene | ABS50N Datasheet |
| 7240 | Tabriz | Himpact polystyrene | HIPS 7240 Datasheet |
| 6045 | Petro Paak | General Purpose Polystyrene | GPPS-1115 Petropaak |
| 1540 | Tabriz | General Purpose Polystyrene | GPPS 1540 Datasheet |
| 1551 | Takhte Jamshid | General Purpose Polystyrene | 1551 Datasheet |
| 1115 | Petro Paak | General Purpose Polystyrene | GPPS-1115 Datasheet |
| 3160 | Jam | General Purpose Polystyrene | G3160 Datasheet |
| PVC65 | Arvand | Polyvinyl chloride | PVC S65 Datasheet |
| PVC65 | Bandar Imam | Polyvinyl chloride | PVC S65 Datasheet |
Why Polymer Datasheets Matter
A polymer datasheet provides the physical, thermal, and mechanical properties of a plastic material. These properties guide decisions in:
- Product design
- Mold selection
- Quality control
- Supplier comparison
For example, when choosing a grade of ABS for injection molding, knowing the Melt Flow Index (MFI) or Impact Resistance can mean the difference between product success or failure.
For Iranian-made materials, datasheets are often available directly from manufacturers or reliable distributors. In this post, we highlight the most popular grades and suppliers across the country.
Leading Iranian Petrochemical Companies
Here are some of the most recognized petrochemical companies in Iran that provide polymers with standardized datasheets:
- Bandar Imam Petrochemical Co. (BIPC)
- Arvand Petrochemical
- Ghaed Basir Petrochemical (ABS producer)
- Tabriz Petrochemical Company
- Jam Petrochemical
- Takhte Jamshid Petrochemical
- Petro Paak
- Amirkabir
- Shazand (Arak)
- Marun and Mobin Petrochemical
- NPC (National Petrochemical Company)
These companies produce a wide range of polymer types with competitive pricing in both rial and dollar terms.
Sample of a polymer product datasheet.
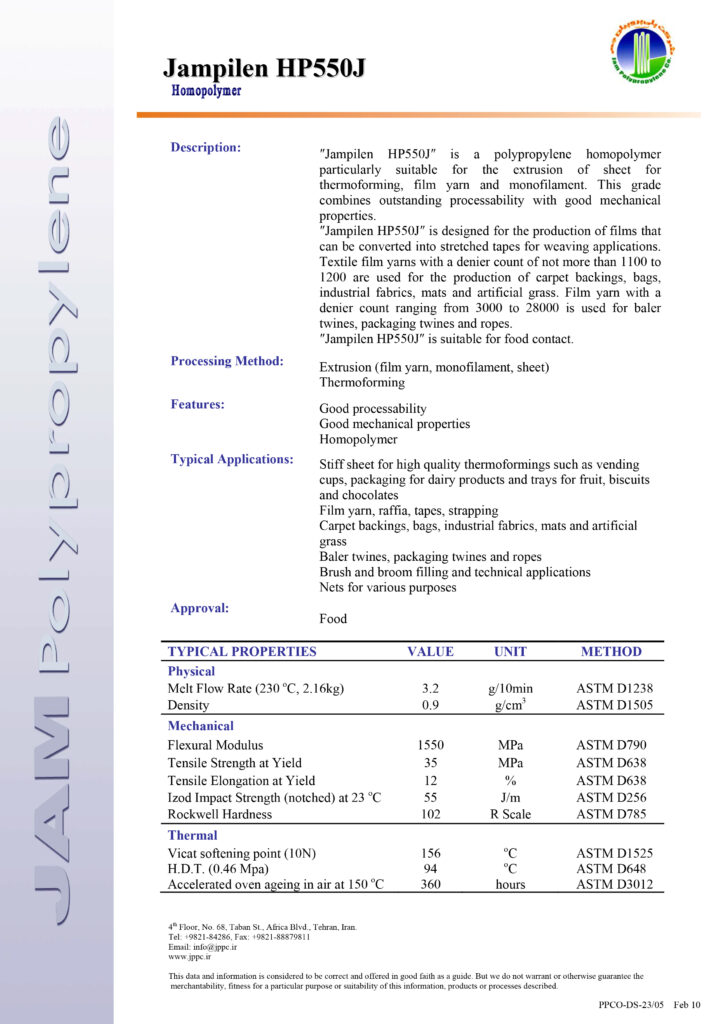
1. Polyethylene (PE)
Polyethylene is the most widely used plastic in the world and comes in three main forms:
a) HDPE – High-Density Polyethylene
HDPE is strong, rigid, and used for bottles, pipes, and containers.
Common Grades:
- HDPE 6045 – Petro Paak
- HDPE 7240 – Tabriz
Sample Datasheet (HDPE 6045):
| Property | Value | Unit | Test Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Melt Flow Index (MFI) | 0.3 | g/10 min | ASTM D1238 |
| Density | 0.954 | g/cm³ | ASTM D1505 |
| Tensile Strength | 25 | MPa | ASTM D638 |
| Flexural Modulus | 1200 | MPa | ASTM D790 |
b) LDPE – Low-Density Polyethylene
LDPE is flexible and used for films, bags, and cable coatings.
Common Grades:
- LDPE 2420D – Bandar Imam
- LDPE 2426H – Imam Khomeini
LDPE datasheets typically show:
- MFI range: 0.3–0.7
- Vicat Softening Temp: ~90°C
- Elongation: >400%
c) LLDPE – Linear Low-Density Polyethylene
LLDPE blends flexibility with strength and is used in stretch films and liners.
Popular Grades:
- LLDPE 22B02 – Bandar Imam
- LLDPE 31B00 – Shazand
2. Polypropylene (PP)
Polypropylene is a versatile polymer used in packaging, textiles, automotive parts, and more.
Key Types:
- Homo-PP – Used in rigid products
- Random Copolymer – For transparency and toughness
- Impact Copolymer – For automotive and durable items
Popular Iranian Grades:
- PP 1540 – Tabriz Petrochemical
- PP 1115 – Petro Paak
- PP 3180 – Jam
Sample Datasheet (PP 1540):
| Property | Value | Unit | Test Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Melt Flow Index (MFI) | 3 | g/10 min | ASTM D1238 |
| Density | 0.90 | g/cm³ | ASTM D792 |
| Tensile Strength | 34 | MPa | ASTM D638 |
| Vicat Softening Point | 152 | °C | ASTM D1525 |
3. ABS – Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene
ABS is a tough, impact-resistant plastic used in consumer electronics, automotive parts, and toys.
Main Iranian Source: Ghaed Basir Petrochemical Co.
Popular Grades:
- ABS N45 – Injection molding
- ABS 10720(W) – Higher MFI for thinner parts
- ABS 10415 / 10417 – General purpose
Sample Datasheet (ABS 10720):
| Property | Value | Unit | Test Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| MFI (220°C, 10kg) | 32 | g/10 min | ASTM D1238 |
| Density | 1.04 | g/cm³ | ASTM D792 |
| Izod Impact (Notched) | 21 | kJ/m² | ASTM D256 |
| Vicat Temp | 98 – 102 | °C | ASTM D1525 |
4. PVC – Polyvinyl Chloride
PVC is used in pipes, fittings, window profiles, and cables.
Types of Iranian PVC:
- PVC S65 – Suspension grade (K value ~65)
Main Producers:
- Arvand Petrochemical
- Bandar Imam Petrochemical
Sample Datasheet (PVC S65 Arvand):
| Property | Value | Unit | Test Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| K Value | 65 | — | DIN 53726 |
| Bulk Density | 0.53 | g/cm³ | ISO 60 |
| Volatile Content | <0.3 | % | ASTM D3030 |
| Particle Size (63µm) | >95 | % | ISO 565 |
5. GPPS – General Purpose Polystyrene
GPPS is transparent and brittle, used in CD cases, cutlery, and packaging trays.
Key Iranian Producers:
- Tabriz Petrochemical
- NPC via agents
Typical Properties:
- MFI: 6–10
- Density: 1.04–1.06 g/cm³
- Vicat: 95°C
- Tensile Strength: 40–50 MPa
6. HIPS – High Impact Polystyrene
HIPS is modified with rubber to improve impact strength, ideal for food containers, toys, and appliance parts.
Features:
- Impact Resistance: High
- Opacity: Opaque (unlike GPPS)
- MFI: 3–6
HIPS is often produced alongside GPPS by the same companies.
How to Read a Polymer Datasheet
Here’s what to focus on in a polymer datasheet:
| Term | Meaning |
|---|---|
| MFI (Melt Flow Index) | Flowability — higher MFI = more fluid in molding |
| Density | Mass per volume — affects strength and stiffness |
| Tensile Strength | How much pull a material can handle |
| Impact Strength | Resistance to sudden shock loads |
| Vicat Softening Temp | The temperature where plastic starts softening |
| Flexural Modulus | Stiffness during bending |
Sourcing Iranian Polymers with Datasheets
Many Iranian suppliers offer downloadable PDF datasheets on their websites or via email upon request. Some include:
- Ghaed Basir Co. for ABS: ghaedbasir.com
- BIPC for HDPE and LDPE: bipc.ir
- Tabriz Petrochemical for PP and PS grades
- Arvand for PVC: arvandpetro.ir
Also, distributors and technical sellers often include datasheet links in their product listings.
Conclusion
Whether you’re sourcing raw material for injection molding, film extrusion, or blow molding, understanding the polymer datasheets of Iranian petrochemical products is crucial. From HDPE 6045 and PP 1540 to ABS 10720 and PVC S65, each material brings its own properties and strengths.
By using the datasheets provided by companies like Ghaed Basir, Tabriz, Petro Paak, and Bandar Imam, you ensure better product design, improved quality control, and optimized cost.
Looking for Datasheets with Prices?
Contact Toosplast Group for updated polymer datasheets or help comparing materials for your specific application. Whether you’re working with ABS, PP, PE, PVC, GPPS, or HIPS, we’ll guide you to the right grade with complete data and prices in Polymer Products Prices in Iran Market
- Published in Uncategorized
Polymer Compound
Polymer Compounds: A Comprehensive and Detailed Overview
Introduction
Polymer compounds are one of the most critical materials in modern engineering and advanced industries, revolutionizing various fields with their unique properties. These materials have found widespread applications in industries ranging from automotive to electronics and even packaging. In this article, we will delve deeper into polymer compounds, their various types, properties, production challenges, and the latest innovations and advancements in this field.
Definition and History of Polymer Compounds
A polymer compound is a composite material made by blending different polymers with specialized additives to achieve desired properties. The production of these compounds has gained attention since the mid-20th century, coinciding with the growth of the plastics industry and the need for lighter, more resilient materials. The history of polymer compound production dates back to the post-World War II era when the need for innovative materials in various industries led to extensive research and development.
Importance of Polymer Compounds in Industries
Polymer compounds have become indispensable in various industries due to their lightweight, high strength, and customizable physical and chemical properties. In the automotive industry, these materials serve as excellent substitutes for heavy metals, reducing vehicle weight, improving fuel efficiency, and lowering greenhouse gas emissions. In electronics, polymer compounds are used as thermal and electrical insulators, playing a crucial role in protecting sensitive electronic components.
Key Properties of Polymer Compounds
One of the primary reasons polymer compounds have become so popular in industries is their ability to improve and adjust mechanical, thermal, and electrical properties. These properties can be tailored according to the specific needs of each industry and application. For example, adding nanoparticles to a polymer compound can enhance its antimicrobial, anti-corrosion, and even electrical conductivity properties. This flexibility allows engineers and designers to create materials precisely suited to the requirements of their specific projects.
Mechanical Strength: Polymer compounds can achieve exceptional mechanical strength by incorporating materials such as glass fibers. This is particularly important in industries like automotive, where resistance to impact and bending is crucial.
Thermal Resistance: Another key feature of polymer compounds is their resistance to heat. With additives like antioxidants and thermal stabilizers, these materials can be designed to perform well even at high temperatures.
Chemical Properties: Polymer compounds can be resistant to various chemicals, including acids, bases, and solvents. This makes them ideal for applications exposed to corrosive environments.
Electrical and Thermal Conductivity: A growing area of research in polymer compounds is enhancing their electrical and thermal conductivity. By adding metal or graphene nanoparticles, these properties can be improved, making them highly valuable in electronics and energy industries.
Types of Polymer Compounds
Polymer compounds can be categorized into various types, each with unique properties and applications:
Thermoplastic Compounds: These compounds are widely used in industries like packaging and automotive due to their ability to be melted and reshaped. Base polymers such as polypropylene and polyethylene are commonly used in producing these compounds.
Elastomeric Compounds: These polymer compounds are highly elastic and can return to their original shape after deformation, making them ideal for products like car tires and flexible components.
Thermal Compounds: These compounds exhibit high thermal stability and are used in industries where high temperatures are involved in production or application.
Specialized Compounds: In addition to the above, specialized polymer compounds are designed for specific applications. These can include flame-retardant, UV-resistant, and antibacterial compounds, each applicable in fields such as medicine, agriculture, and construction.
Production Process of Polymer Compounds
Producing polymer compounds requires technical expertise and extensive experience in material blending and engineering processes. The main steps in production include:
Selection of Base Polymer: The first step in producing a polymer compound is selecting a base polymer that determines the material’s fundamental properties. Base polymers can include polyethylene, polypropylene, polycarbonate, and more.
Selection of Additives: The additives used in a polymer compound should be selected based on the specific needs of each application. These additives may include reinforcing fibers, antioxidants, thermal stabilizers, and more.
Mixing and Blending: The next step involves combining the selected materials. This process can include mixing, melting, and extrusion to ensure uniform distribution of additives throughout the base polymer.
Shaping and Processing: After blending, the polymer compound is shaped into its final form. This process can involve extrusion, injection molding, or other methods, depending on the final product.
Testing and Quality Control: Finally, the finished product must be tested for quality and performance. These tests may include assessing mechanical, thermal, and chemical properties to ensure the polymer compound meets the desired standards.
Diverse Applications of Polymer Compounds
Due to their versatility and customizable properties, polymer compounds are used in numerous industries:
Automotive: In the automotive industry, polymer compounds help reduce vehicle weight, improve fuel efficiency, and lower greenhouse gas emissions. Components such as bumpers, dashboards, and interior parts are widely made from these materials.
Electronics: In the electronics industry, polymer compounds serve as thermal and electrical insulators and are used in components such as mobile phone cases, televisions, and laptops.
Packaging: In the packaging industry, polymer compounds are popular due to their lightweight, impact resistance, and ability to preserve the properties of packaged goods.
Medical: In the medical industry, polymer compounds are used to produce medical equipment such as syringes, blood transfer tubes, and surgical device components. These materials are ideal for this sensitive industry due to their antibacterial properties and sterilization capabilities.
Construction: In the construction industry, polymer compounds are used to produce insulation materials, pipes, and decorative components. These materials are highly resistant to environmental factors like water and corrosion, making them ideal for construction applications.
Challenges and Recent Innovations in Polymer Compound Production
Despite their numerous advantages and wide-ranging applications, producing polymer compounds presents challenges. Among these are the correct selection of additives and determining their optimal ratios. Additionally, finding ways to increase the recyclability of these materials to reduce environmental impact is another major challenge in this field.
Recent innovations in polymer compound production include using nanoparticles to improve mechanical and thermal properties, developing biodegradable polymer compounds to reduce environmental burden, and designing materials with self-healing capabilities to increase product longevity. These innovations highlight the importance of continuous research and development in this field and the ongoing efforts to enhance the features and applications of polymer compounds.
Future of Polymer Compounds
The future of polymer compounds is closely tied to technological advancements and the growing demands of various industries. With the development of new technologies such as 3D printing, the use of polymer compounds in producing complex and customized components is expected to rise significantly. Furthermore, with increasing environmental awareness and stricter regulations, there will likely be a greater focus on producing biodegradable and recyclable polymer compounds.
Conclusion
Polymer compounds are one of the key materials in advanced industries, playing a critical role in the development and advancement of modern technologies. Given their unique properties and customizable features, the use of polymer compounds is expected to continue growing in the future. On the other hand, the challenges and issues related to the production and recycling of these materials require further research and development to ensure they remain a sustainable and efficient option in various industries. At Toosplast, we take pride in offering premium quality polymer compounds tailored to meet the specific needs of our clients across various industries. With a commitment to innovation, precision, and sustainability, our products are designed to exceed the highest industry standards. Whether you are looking for thermoplastic compounds or specialized polymer materials, we provide customized solutions that deliver exceptional performance and reliability. Partner with us to experience unparalleled quality and expertise in the world of polymer compounds, where every product is crafted with care to ensure your success.
- Published in Uncategorized
Toosplast Legacy and Products

About Company
With over half a century of excellence in the polymer and plastic industry, amizehaye Polymeri Toos stands as a beacon of quality and innovation. Established with a commitment to delivering superior polymer compounds, we have consistently set benchmarks in the field, ensuring that our products meet the highest standards of quality and performance.
Founded over 50 years ago, Toos Plast has grown to become a leader in the polymer and plastic industry. Our extensive experience and deep-rooted expertise have enabled us to perfect the art and science of polymer compound manufacturing. Our products are meticulously crafted from the best raw materials and formulated using state-of-the-art techniques, ensuring unmatched reliability and efficiency.
At Toos Plast Group, we take pride in our global footprint. We produce and supply a diverse range of polymer compounds to various countries, catering to the unique needs of different markets. Our international presence is a testament to the trust and confidence our clients place in our products, underscoring our commitment to quality and excellence.
Quality is the cornerstone of Toos Plast. Our commitment to using the best raw materials, high accuracy in quality control process and adhering to the best formulation practices ensures that our products meet international industry standards.
Toos Plast is based in Iran. This proximity to high-quality raw materials, combined with our advanced manufacturing capabilities and strategic location of Iran including access to the ocean, positions Toos Plast Group as a leading player in the polymer and plastic industry.
At Toos Plast, innovation and sustainability go hand in hand. We are dedicated to developing eco-friendly solutions and adopting sustainable practices in our operations. Our forward-thinking approach ensures that we remain at the forefront of technological advancements in the polymer industry, continually offering products that are both innovative and environmentally responsible.
Toos Plast Company’s rich legacy, commitment to quality, and strategic vision have cemented our reputation as a trusted supplier of premium polymer compounds. We look forward to continuing our journey of innovation and excellence, delivering top-tier products to our valued clients around the world
Our Products
High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE)
HDPE is known for its exceptional strength-to-density ratio, making it the ideal choice for a wide range of applications, from robust containers and pipes to high-performance geomembranes. Our HDPE granules are manufactured with precision, ensuring consistency, durability, and superior performance. For viewing HDPE granules and grades please click on links below:
Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE)
LDPE offers unmatched flexibility and resilience, making it perfect for applications requiring pliability and resistance to impact. From packaging films and coatings to squeezable bottles and toys, our LDPE granules provide the reliability and versatility needed for modern manufacturing demands. For viewing LDPE granules and grades please click on links below:
Linear Low-Density Polyethylene (LLDPE)
Combining the benefits of LDPE and HDPE, LLDPE offers enhanced tensile strength and puncture resistance while maintaining flexibility. Ideal for film applications, such as stretch wrap, agricultural films, and food packaging, our LLDPE granules are engineered to meet the highest standards of quality and performance. For viewing LLDPE granules and grades please click on links below:
Why Choose Us?
Quality Assurance
At Toos Plast, quality is our top priority. Our state-of-the-art production facilities and rigorous quality control processes ensure that every batch of polyethylene granules meets the highest industry standards. We are dedicated to providing products that our customers can rely on.
Contact Us
Ready to learn more about our polyethylene products? Contact us today to discuss how Toos Plast can help you achieve your production goals with our premium HDPE, LDPE, and LLDPE granules.
+982156546700
commercial@toosplast.com


- Published in Uncategorized
The difference between polyethylene and polypropylene
Two types of the most widely used raw materials in the plastic industry are polyethylene and polypropylene. Each of these two materials has unique uses. These two materials are in the category of thermoplastic and semi-crystalline polymers, which are widely used in various industries. Other raw materials are also used in the plastic industry, which are used in low tonnage due to their high cost. In this article, we will examine the difference between polyethylene and polypropylene.
Polyethylene (PE)
Polyethylene is one of the most widely used polymers in the world, which belongs to the polyolefin family and belongs to the thermoplastic category. This material is one of the thermoplastic polymers; In this way, when it reaches the melting point, it turns into a liquid state and when it reaches the freezing point, it turns into a solid state. Polyethylene contains a very simple structure, so that it is simpler than all commercial polymers. A polyethylene molecule is a long chain of carbon atoms with two hydrogen atoms attached to each carbon atom.
polypropylene (pp)
Polypropylene is the second most widely used thermoplastic in various industries, which recently in granulated form can bring more applications in the production of products. Polypropylene (often referred to as PP textile is used to produce cable and wire covers, bottles, cans, etc.Polypropylene), is a special structure of polypropylene polymer that is used in the form of balls (grains) to produce different products in different forms. Takes. known as chemical PP
The difference between polyethylene and polypropylene
- Polypropylene is stiffer than polyethylene and is used more for the production of molded parts.
- The cracking resistance of polypropylene is high, but polyethylene is somewhat elastic and has more flexibility.
- In polypropylene, due to the low rate of crystallization, the presence of nucleating agents will be effective, while in polyethylene, due to the high rate of crystallization, the presence of nucleating agents is less effective. Therefore, it is more possible to produce a transparent product in polypropylene.
- The printability of polypropylene films is more than that of polyethylene, and in polyethylene film, it is only possible if the surface is modified.
- The melting point of polypropylene is higher than polyethylene and they are used in the production of structural plastics and fibers.
- The impact resistance and physical properties of polyethylene are such that it is more stable against cold and is used in the construction of traffic signs. On the other hand, polypropylene has high fatigue resistance and is suitable for making hinges.
- Polyethylene is more resistant to UV light than polypropylene.
- The chemical resistance of polypropylene against organic solvents, acids and electrolytes is much higher than that of polyethylene.
- The static electricity charge of polyethylene is lower than that of polypropylene and it is a good electrical insulator. Therefore, the use of antistatic masterbatch is recommended for polypropylene-based products.
- Polymerization of linear type of polyethylene is difficult and by controlling the conditions, it is possible to produce the final product with high purity. But the polymerization of high purity polypropylene is simpler.
- The use of polyethylene is usually 100% pure, but polypropylene is generally copolymerized with polyethylene. This copolymer is flexible and is used in making synthetic paper. Synthetic paper is tear and water resistant.
The difference between polyethylene and polypropylene in terms of structure
The main difference between these two polymers originates from their monomer units. Polypropylene is made from a mixture of propylene monomers and polyethylene from a mixture of ethylene monomers. The chemical formula of polypropylene is (C3H6)n and polyethylene is (C2H4). The monomer unit of polyethylene and polypropylene can be seen in the following figure:
The difference between polyethylene and polypropylene in terms of physical and mechanical properties
Similarities of polyethylene and polypropylene
Polyethylene and polypropylene have some common properties, such as long life, high quality and flexibility are these features that have made To be used as a widely used polymer raw material in most sectors and industries. Also, both are composed of fibers called olefins, which when combined with other materials, produce oily liquids. Both polymers are recyclable, but the recyclability of polyethylene is better than polypropylene. The signs of polyethylene and polypropylene recycling are as follows:
Conclusion
In order to use all kinds of raw materials, it is better to choose and buy these products by knowing the type of application and desired product, in order to avoid suffering secondary economic losses. In general, although polypropylene granules and polyethylene granules have several physical They are, but they are completely different in terms of nature and usage. PP is more flexible and PE is stronger. PP is also elastic in nature but PE is stable. However, in the end, both plastic products are important and widely used according to their share in the market.
- Published in Uncategorized
Polymers widely used in making bottles
Polyethylene Terephthalate, which is one of the most widely used thermoplastic polymers in the world, is used to make all kinds of bottles. In the textile industry, this polymer is known as polyester. In the food and beverage packaging industry, it is referred to as PET or PET resin. In the past, another type called PET-P was used in the clothing industry, which has almost stopped being used today.
Polymers widely used in making bottles
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) is a polymer that is used in most countries to produce polyester fibers (70 percent), bottle resin (22 percent), film (6 percent) and engineering polyester resins (2 percent), but in Iran this polymer It is mostly used to make all kinds of drinking bottles. Due to the high resistance of these bottles against breakage, temperature and gas penetration, low weight and cheap price compared to other packaging materials such as glass and metal, the production of plastic bottles from this material has found wide use.
Characteristics of granular pet
Granule PET is a suitable waterproofing agent. Granule PET is a safe, strong, light, flexible and non-toxic material that can be easily recycled. The presence of all these features in one product has attracted the attention of all people working in the field of packaging to this product. Among the features that have led to the use of this product in the packaging of food and beverages, we can mention its lightness, strength, preservation of health and freshness of the product, and the fact that it cannot be crushed. One of the main uses of this product is its use in mineral water and carbonated soft drinks.
Advantages and disadvantages of granule PET (polyethylene terephthalate)
These polymers are easily available and cheap.
PET polymers are resistant to moisture and organic substances, water and chemicals.
The ratio of their resistance to their weight is very high.
They are very transparent and unbreakable. (They don’t break like glass packages.)
Polyethylene tereflat is easily recyclable. PET plastic is one of the types of recycled plastics that are used to produce products such as containers, sleeping bag insulation, polyester fabrics and carpets, etc.
PET plastics are not biodegradable. This can be good or bad depending on their application.
PET polymer has lower thermal resistance than other polymers.
1- Polyethylene terephthalate BG781
Polyethylene terephthalate (BG781 (BG780S) is a bottle-grade polyethylene terephthalate (PET) produced during the process of continuous melt polymerization along with solid state polymerization. BG781 material has excellent transparency and gloss and very good toughness and is resistant to oxygen penetration And carbon dioxide is very resistant.Its applications are in oil and mineral water bottles and all kinds of small jars.
Feature Pat BG781
It has excellent transparency and gloss and very good toughness and is very resistant to the penetration of oxygen and carbon dioxide.
Application of PET BG781
Bottles of mineral water, edible oil
2- Polyethylene terephthalate BG825
Polyethylene terephthalate (BG825 (BG820N) is a bottle-grade polyethylene terephthalate (PET) produced during the process of continuous melt polymerization along with solid state polymerization. And carbon dioxide is very resistant.Its applications are in carbonated beverage bottles.
Feature Pat BG825
It has excellent transparency and gloss and very good toughness and is very resistant to the penetration of oxygen and carbon dioxide.
Application of PET BG825
Bottles of carbonated drinks
Conclusion
Polymer materials are widely used in the production of nylon and also in the production of disposable containers and bottles. In this article, we got to know the most commonly used grades in bottle making.
- Published in Uncategorized
The widely used polymer grades in the production of nylon types
Different polymer grades are used to produce nylon. In this article, we are going to investigate the widely used polymer grades in the production of nylon types.
1- 2100 light polyethylene
Polyethylene 2100TN00 or material 2100 is a film-grade light polyethylene that is used to produce high durability films and high strength packaging liners.
Features of polyethylene 2100
High durability and high strength
Application of 2100 materials
To produce movies
2- Light polyethylene 0190
Material 0190 or polyethylene LF0190 is a film-grade light polyethylene with high molecular weight, which is used to produce various films and types of liners.
Features of polyethylene 0190
High molecular weight
Application of materials 0190
It is used to produce nylon and polyethylene film.
3- Light polyethylene 2101TN
Polyethylene 2101TN47 or 2101TN material is a film grade light polyethylene. This grade has no additives and has high tensile and toughness properties.
Features of polyethylene 2101TN
High tensile properties and toughness
Application of 2101TN materials
To produce high-speed shrink films
4- Light polyethylene 2420E
Polyethylene 2420E or 2420E material is a light polyethylene (LDPE) which is used for the production of packaging and shrink films due to its high transparency.
Features of polyethylene 2420E
High transparency
Application of 2420E materials
To produce shrink films
5- Light polyethylene 0075
Polyethylene LH0075 is a film grade light polyethylene. 0075 material, having good mechanical properties, is used for the production of food, pharmaceutical, shrink and industrial packaging films, as well as air molding of small bottles.
Feature of light polyethylene LH0075
Good mechanical properties
Application of material 0075
It is used to produce all kinds of polyethylene films, such as shrink film, big and small bottles that hold medicine and chemicals, food packaging, etc.
6- Linear style polyethylene 235F6
Polyethylene 235F6 is a linear light polyethylene (LLDPE) produced by gas process. 235F6 material is used for the production of agricultural, industrial and food films due to its good mechanical properties and processability.
Features of polyethylene 235F6
Melt strength and high tensile strength
Application of 235F6 materials
Different types of agricultural films and tapes
7- Linear light polyethylene 22B02
Polyethylene 22B02 or material 22B02 is a linear light polyethylene (LLDPE) which is used to produce all kinds of films for industrial and food packaging due to its strength and high tensile properties.
Features of polyethylene 22B02
High strength, low density
Application of material 22B02
To produce all kinds of films for industrial and food packaging
8- Light linear polyethylene 0209KJ
Polyethylene LL0209KJ or material (0209KJ (209) is a light linear polyethylene with normal butene and contains antioxidant and antiblock additive. This grade is used for general purposes of producing all kinds of films (Film) and is often mixed with other polyethylene grades. Light ethylene is used.The resulting films have more tensile strength and tear resistance by adding this grade.
Feature of linear light polyethylene 0209KJ
Higher tensile strength, better sealing
Application of 0209KJ materials
For the production of food, industrial and agricultural packaging films
9- heavy polyethylene EX5
EX5 material or polyethylene (EX5 (9450F) is a heavy polyethylene (HDPE) with a high molecular weight copolymerized with 1-butene. Its high tensile strength makes it suitable for the production of all kinds of plastic bags and packaging films.
Feature PE EX5
High molecular weight copolymerized with 1-butene and high tensile strength
Application of EX5 materials
Disposable gloves, freezer bags, food and fruit bags, garbage bags
10- F7000 heavy polyethylene
Material F7000 (polyethylene 7000F) is a heavy polyethylene for producing very thin films. Polyethylene or polyethylene is one of the simplest and cheapest polymers, and polyethylene is a waxy and inactive solid. This material is obtained from the polymerization of ethylene and is briefly shown as PE.
F7000 polyethylene feature
High molecular weight and high film strength
Application of F7000 material
Advanced Ultra Thin Film
single-use glove
freezer bag
Bag for carrying food and fruit
garbage bag
Medical Gowns
Making safety equipment
Construction of water tanks
Making toys
Making pipes and fittings
Production of plastic parts
- Published in Uncategorized